# Creating a JS Console
As a little example, we will create a JS console. We need an input field where the user can enter his JS expressions and ideally there should be a list of output results. As this should more look like a desktop application we use the Qt Quick Controls module.
TIP
A JS console inside your next project can be really beneficial for testing. Enhanced with a Quake-Terminal effect it is also good to impress customers. To use it wisely you need to control the scope the JS console evaluates in, e.g. the currently visible screen, the main data model, a singleton core object or all together.
We use Qt Creator to create a Qt Quick UI project using Qt Quick controls. We call the project JSConsole. After the wizard has finished we have already a basic structure for the application with an application window and a menu to exit the application.
For the input, we use a TextField and a Button to send the input for evaluation. The result of the expression evaluation is displayed using a ListView with a ListModel as the model and two labels to display the expression and the evaluated result.
Our application will be split in two files:
JSConsole.qml: the main view of the appjsconsole.js: the javascript library responsible for evaluating user statements
# JSConsole.qml
# Application window
// JSConsole.qml
import QtQuick
import QtQuick.Controls
import QtQuick.Layouts
import QtQuick.Window
import "jsconsole.js" as Util
ApplicationWindow {
id: root
title: qsTr("JSConsole")
width: 640
height: 480
visible: true
menuBar: MenuBar {
Menu {
title: qsTr("File")
MenuItem {
text: qsTr("Exit")
onTriggered: Qt.quit()
}
}
}# Form
ColumnLayout {
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 9
RowLayout {
Layout.fillWidth: true
TextField {
id: input
Layout.fillWidth: true
focus: true
onAccepted: {
// call our evaluation function on root
root.jsCall(input.text)
}
}
Button {
text: qsTr("Send")
onClicked: {
// call our evaluation function on root
root.jsCall(input.text)
}
}
}
Item {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
Rectangle {
anchors.fill: parent
color: '#333'
border.color: Qt.darker(color)
opacity: 0.2
radius: 2
}
ScrollView {
id: scrollView
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 9
ListView {
id: resultView
model: ListModel {
id: outputModel
}
delegate: ColumnLayout {
id: delegate
required property var model
width: ListView.view.width
Label {
Layout.fillWidth: true
color: 'green'
text: "> " + delegate.model.expression
}
Label {
Layout.fillWidth: true
color: delegate.model.error === "" ? 'blue' : 'red'
text: delegate.model.error === "" ? "" + delegate.model.result : delegate.model.error
}
Rectangle {
height: 1
Layout.fillWidth: true
color: '#333'
opacity: 0.2
}
}
}
}
}
}# Calling the library
The evaluation function jsCall does the evaluation not by itself this has been moved to a JS module (jsconsole.js) for clearer separation.
import "jsconsole.js" as Utilfunction jsCall(exp) {
const data = Util.call(exp)
// insert the result at the beginning of the list
outputModel.insert(0, data)
}TIP
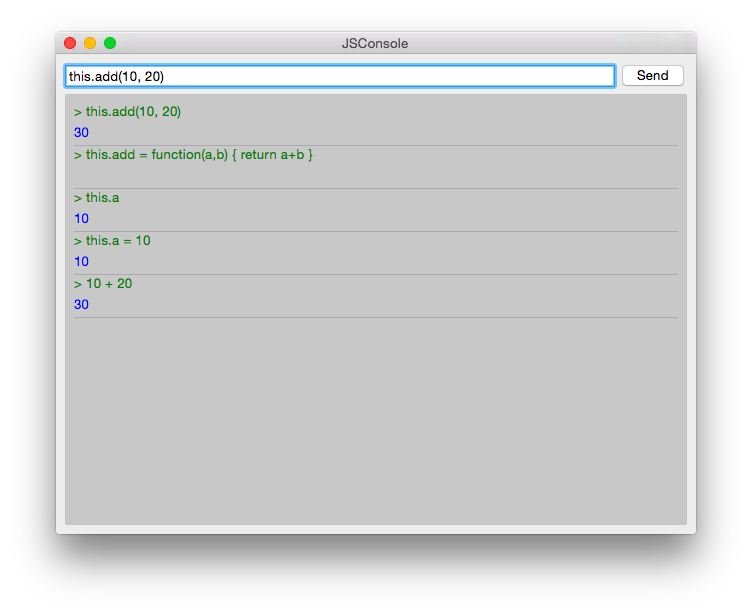
For safety, we do not use the eval function from JS as this would allow the user to modify the local scope. We use the Function constructor to create a JS function on runtime and pass in our scope as this variable. As the function is created every time it does not act as a closure and stores its own scope, we need to use this.a = 10 to store the value inside this scope of the function. This scope is set by the script to the scope variable.
# jsconsole.js
// jsconsole.js
.pragma library
const scope = {
// our custom scope injected into our function evaluation
}
function call(msg) {
const exp = msg.toString()
console.log(exp)
const data = {
expression : msg,
result: "",
error: ""
}
try {
const fun = new Function('return (' + exp + ')')
data.result = JSON.stringify(fun.call(scope), null, 2)
console.log('scope: ' + JSON.stringify(scope, null, 2), 'result: ' + data.result)
} catch(e) {
console.log(e.toString())
data.error = e.toString()
}
return data
}The data return from the call function is a JS object with a result, expression and error property: data: { expression: "", result: "", error: "" }. We can use this JS object directly inside the ListModel and access it then from the delegate, e.g. delegate.model.expression gives us the input expression.
← JS Objects Qt and C++ →